Hemp Biomass for Bioenergy Production: Is it Safe?
Spent hemp biomass is generally considered waste in agriculture, but the truth is that it is far from useless. In this article, we inform you on the hidden economic value of hemp biomass for bioenergy production.

Spent hemp biomass is generally considered waste in agriculture, but the truth is that it is far from useless. In fact, spent biomass can also be extremely profitable for farmers who know how to use it. In this article, we inform you on the hidden economic value of hemp biomass for bioenergy production.
The term "hemp biomass" has many alternative definitions. Broadly speaking, hemp biomass refers to dried, extraction-grade industrial hemp and is the basic raw material for most cannabinoid extracts, isolates, and distillates. Biomass in this context refers to the mature, CBD-rich flowers produced by hemp plants.
Some manufacturers also use the term “biomass” to refer solely to the non-floral by-products that result from the production of high-CBD hemp flowers. By this is meant the excess biological material, such as stems, cuttings and leaves, that remain after the buds have grown. Sometimes, the total weight produced by hemp plants is also referred to as “biomass”.

Normally, CBD-rich hemp biomass is used to produce CBD extracts. Alternatively, hemp residue material can also be harvested for its fibers, which are useful from various industrial perspectives.
The type of biomass a hemp plant produces most depends on the strain: Hemp oilseed strains include shorter plants that are rich in seeds, while fiber strains include taller plants that are rich in stalks. While some are used in food production, others are used in the manufacture of textiles. Oilseed strains have a high concentration of cannabinoid-rich bud material. The vast majority of fibrous biomass is not made from CBD-rich hemp, but from low-cannabinoid hemp strains grown for their seeds.
The hemp biomass harvesting process varies slightly by plant species, and the exact procedure depends on whether fiber or oilseed hemp is being harvested.

Fiber-rich hemp biomass needs to be roasted to break down the cellular tissue so that the fibers can be easily removed from the stem. The stem consists of two parts: the bast and the shives. The bast is woven into fibers, while the shives are commonly used for insulation, building materials, and paper that do not require long fibers.
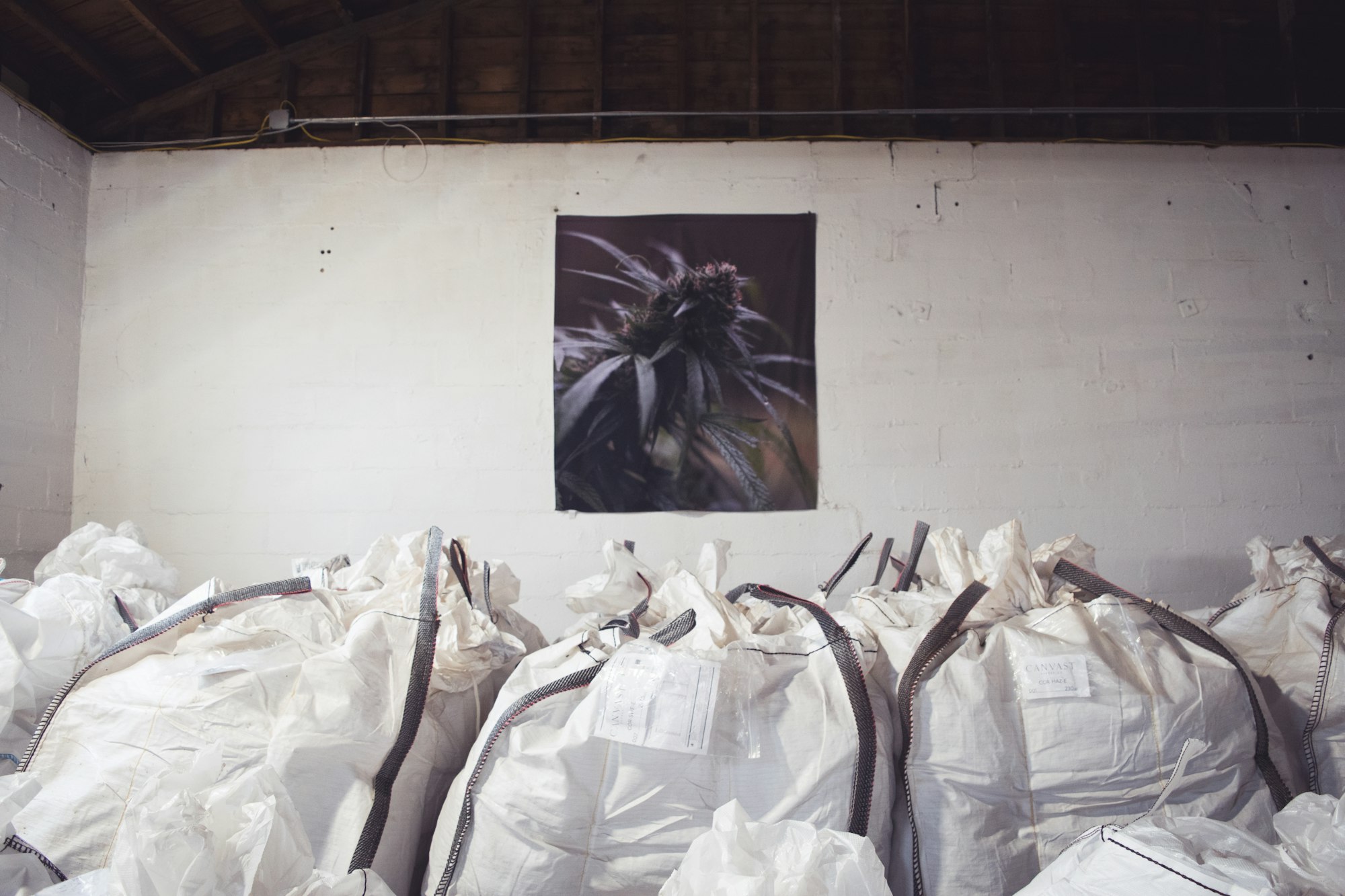
The biomass of oil hemp, on the other hand, must be thoroughly dried before the seeds can be further processed in an oil press. Shredding then breaks down large leaves and stalks into smaller pieces that are easier to pack by the kilo. At Signature Products, hemp biomass is packed in big bags so that it can be shipped in bulk to the extraction facility for further processing.

Hemp biomass is often offered in different qualities. The value of hemp biomass depends on the cannabinoid concentration of the biomass. For example, the lower its potency, the more likely it is that the extracts made from it will contain contaminants. High-quality CBD biomass is generally made with more flower residue and fewer stems, while low-quality CBD biomass is made with more stems and leaves from low-yielding parts of the plant. To ensure consistent quality, we offer cannabinoid (including THC), heavy metal and pesticide analyses for every batch.

As leftover components of hemp are usually discarded after processing, it would be more sustainable to recycle the stems, leaves, and other unused parts of the plant, e.g. for the power generation industry. One of the most exciting and emerging uses for hemp biomass is in bioenergy production. The term bioenergy refers to renewable energy from biological sources, such as biomass, which can be converted into heat or processed into gases or liquids such as ethanol and biodiesel, among other things.

For example, pelleting industrial hemp biomass can produce a heating fuel for pellet stoves in regions with high heating loads. Furthermore, the entire hemp plant biomass—including the stems, seeds, and flowers—can be used to make various types of automotive fuel. Both oilseed and fiber plants would therefore be ideal for this purpose. There are two main types of fuel that can be extracted: hemp biodiesel, which is derived from pressed hemp seed oil, and hemp ethanol/methanol.
To extract ethanol from hemp biomass, it goes through a fermentation and distillation process, while methanol is generally produced from the woody plant material by dry distillation. Converting hemp fiber into fuel is an intensive process because the hemp biomass has to be pre-treated first.

However, at least in a laboratory setting, hemp biofuel has already shown promise: in one study, almost 100% of hemp oil could be converted into biodiesel, proving its high conversion efficiency. Researchers have also used various tests to assess the possibility of using hemp biomass for energy purposes. They concluded that hemp biomass proves to be a valuable energy source, which in terms of its technical and chemical properties is even comparable to the plant energy sources already used.
Industrial hemp could have many advantages as an energy crop compared to its competitors as it brings many outstanding traits, a study notes: The cost of growing this undemanding crop is low, it has a high dry matter yield and high lignocellulose content. The variety-specific adaptability of hemp to different climate zones and soils also makes it a suitable bioenergy raw material. In addition, the plant is also able to pull toxic chemicals out of the soil via phytoremediation and thus improve soil health:

The supply of industrial hemp biomass to a local biorefinery for conversion to bioenergy could potentially become a very large market under the right conditions - if biorefineries were made available in the respective regions in the future.
Contaminated Hemp Biomass for Bioenergy?
According to various studies, hemp is not only a suitable bioenergy raw material, but also an extremely efficient phytoremediator for soils contaminated with heavy metals and radionuclides. This circumstance could possibly offer an opportunity to benefit twice from the cultivation of the hemp plant: through bioenergy production as well as soil decontamination.
According to a paper published in August 2022, implementing a regional bioenergy system could not only effectively utilize a country's biomass, but also significantly reduce the overall use of fossil fuels. Researchers from ETH Zurich also highlight that many people living near contaminated sites could find alternative income through phytomanagement. Further research concluded that contaminated hemp biomass can yield significant amounts of bioenergy, thus offering the opportunity to convert contaminated soils into usable and productive areas.

According to another study, harvested plant biomass can be converted into energy in two main ways: 1) thermochemical conversion including pyrolysis, gasification and direct combustion; and 2) biochemical conversion including fermentation and anaerobic digestion.

However, the biggest challenge when using contaminated biomass is its heavy metal content, which can cause secondary pollution if bioenergy production and disposal is improper, as researchers point out. In one of our Linkedin posts, in which we reported on the ability of hemp to clean up contaminated soil using phytoremediation, a lively discussion has erupted on this topic. Some users expressed their concerns about how contaminated hemp biomass could harm the environment if used for further processing into bioenergy:
"You’re telling people to concentrate toxins then aerosolize them by burning as fuel so we can all breathe them?" - Linkedin-User
However, research is already being done to get this problem under control with the correct handling of end products of phytoremediation. A book was published in 2017, dealing in detail with the energy-producing potential of phyto-remediator plants, including hemp. According to a paper, various disposal and recycling methods have already been developed, including heat treatment, extraction treatment, microbial treatment, compression landfills and synthesis of nanomaterials. There are many individual factors to consider when choosing the most appropriate recycling or disposal method.

Two methods for sequestering contaminants involve the use of adsorption materials and combustion. According to a study, heavy metals can be concentrated in slag, ash and dust particles after biomass combustion. Combustion is currently proving to be the most practical, cost-effective and environmentally friendly processing method. The burned plant matter can also potentially be reused through 'phytomining' for the biological recovery of precious and semi-precious metals.

A study published in 2021 also offered some concrete solutions regarding the pre-treatment of contaminated biomass, such as special sorbents, demineralization - and leaching techniques to remove or immobilize heavy metals. For example, a thermochemical pre-treatment is recommended for hemp biomass in order to convert it biologically into succinic acid. This acid can be used as a precursor for biodegradable polymers, foods, fine chemicals, green solvents and pharmaceuticals. The study also claims that the high quality of hemp fibers and shives is not compromised by metal contamination and can therefore be used in composite materials, among other things.
In summary, the overall environmental impact of bioenergy cultivation on contaminated land depends on the entire cultivation chain, including the management of bioenergy residues, as research also points out. Another study published in 2020, which is investigating the potential of hemp for paired phytoremediation and bioenergy production, advocates the implementation of a closed production system. In this way, contaminated material would be safely disposed of directly on site, while bioenergy would be generated for on-site operations.

